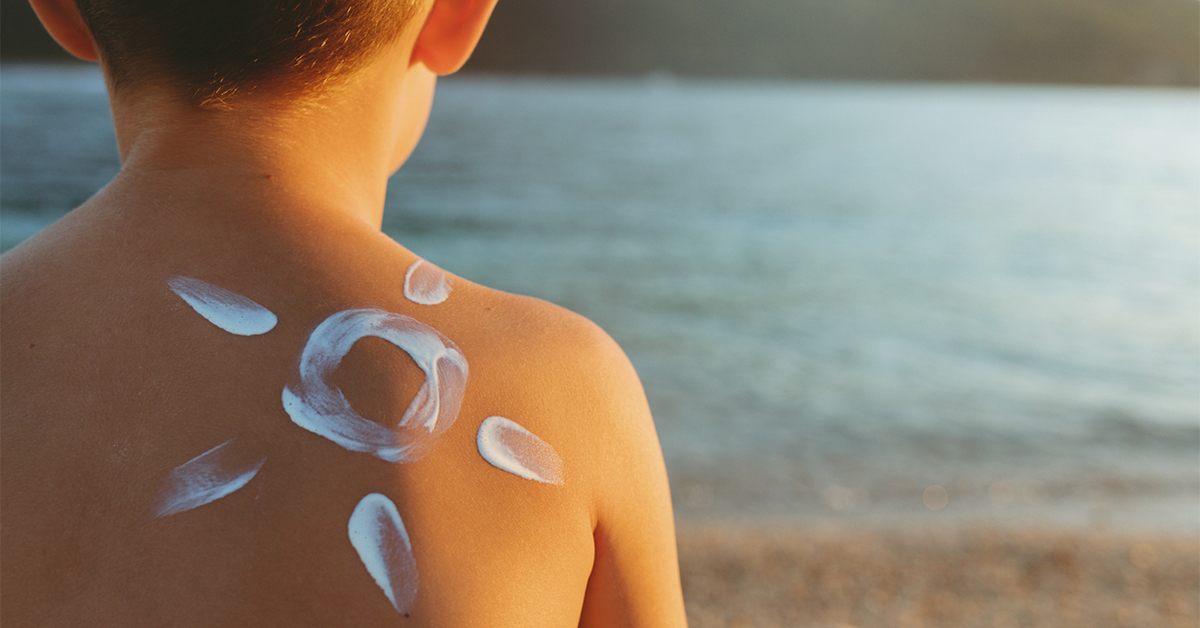
Summer is here, and that means fun in the sun! Before you head out for a day at the lake or a hike in the park, it’s important to know the risks of sun exposure. Unprotected skin can suffer from sunburn, premature aging, and even skin cancer. Read on for everything you need to know about sun protection, from choosing the right sunscreen to applying it effectively.
The power of the sun
The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays can be very damaging to the skin. They can cause sunburn, premature aging, and even skin cancer. Often categorized as UVA or UVB, overexposure to either can be harmful.
- UVA rays have longer wavelengths and penetrate deeper into the skin, affecting collagen and elastin. Damage from these rays can lead to premature skin aging, including wrinkles, sagging, and loss of elasticity.
- UVB rays are shorter and less penetrating than UVA rays. They are absorbed by the skin’s outermost layer, are the primary cause of sunburn, and play a more significant role than UVA rays in developing skin cancer.
Dive deep into the facts with the Skin Cancer Foundation article, UV Radiation & Your Skin.
Why sunscreen matters
Sunscreen acts as a barrier, absorbing or reflecting harmful UV rays to lower your risk. Consistent sunscreen use can significantly reduce your chances of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. You may be surprised to learn Minnesota has one of the highest melanoma rates in the country. While doctors haven’t determined exactly why this is, sunscreen is critical in preventing all skin cancers.
Choosing the right sunscreen
There are two main types of sunscreen: chemical and mineral.
- Chemical sunscreens: Lightweight, easily absorbed, and offer broad-spectrum protection. However, they may irritate some skin types and need frequent reapplication.
- Mineral (or physical) sunscreens: Offer broad-spectrum protection, are less likely to irritate skin, and are considered safe for pregnancy and breastfeeding. They may leave a white cast and feel thicker than chemical sunscreens.
The best sunscreen for you is one that you will actually use. For more on the ongoing debate between chemical and mineral sunscreens, read, What’s the Best Kind of Sunscreen? Whatever you decide is best for you, choose a broad-spectrum (protects against UVA and UVB rays) sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher and apply it generously and frequently.
Understanding SPF
Sun Protection Factor (SPF) indicates how well a sunscreen protects against UVB rays, the cause of sunburn. An SPF 30 sunscreen allows you to stay in the sun 30 times longer than without sunscreen (ideally). However, no sunscreen is perfect, and reapplication is crucial.
Applying sunscreen properly
One-third of Americans don’t use sunscreen, and most only apply 25-50% of the recommended amount. There is no good reason to skimp on sunscreen.
- Apply generously (one ounce or about a shot glass full) to all exposed skin 30 minutes before sun exposure.
- Cover all exposed skin. Remember your ears, the tops of your feet, your scalp (if thinning hair), and the back of your neck.
- Reapply at least every two hours or immediately after swimming or excessive sweating.
The American Academy of Dermatology shares their top recommendations for sun protection in this video:
Sunscreen and outdoor activities
- Swimming and water sports: Choose a water-resistant sunscreen and reapply after swimming.
- Hiking and outdoor adventures: Opt for sweat-resistant, SPF 30+ sunscreen and consider a sunscreen stick for easy reapplication.
- Outdoor sports: Choose lightweight, non-greasy sunscreen that absorbs quickly. Spray sunscreens can be convenient for large areas.
According to the Food and Drug Administration, active individuals should be aware that there are no “waterproof” sunscreens, as all sunscreens wash off in water. “Water-resistant” sunscreen is a more proper term. They typically last 40-80 minutes but must be reapplied to ensure lasting protection.
Protecting children
Children’s skin is more delicate than that of adults. That said, the importance of proper sun protection is even more crucial. Use broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen, apply generously, and reapply frequently. Keep babies under 6 months out of direct sunlight and use protective clothing and shade instead of sunscreen.
“As a family medicine doctor, I see firsthand the impact of sun damage. Sunscreen isn’t just for vacations – it’s a daily essential. Apply broad-spectrum SPF 30+ every day, rain or shine, to protect your skin from premature aging and skin cancer risk. Remember, healthy habits start young, so make sun protection a fun family routine!”
Rachel Dubay, MD
Welia Health Family Medicine Physician
Sun protection for everyone
Regardless of skin tone, everyone needs sun protection. While darker skin has some natural protection, UV rays can still cause damage. Use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, seek shade, and wear protective clothing.
Sunscreen for sensitive skin
Look for gentle, hypoallergenic formulas free of harsh chemicals and fragrances. Mineral sunscreens are often better for sensitive skin. Patch test any new sunscreen before applying it all over.
Sunscreen and medications
Some medications increase sun sensitivity. Common sun-sensitive medications include antibiotics, oral contraceptives, and acne medication. Consult your provider with questions or concerns while taking these medications.
Eco-friendly sunscreen choices
While none of our 10,000 lakes have coral to protect, if you’re headed on a beach vacation, consider using a “reef-safe” sunscreen with mineral ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. These are less harmful to coral reefs and marine life.
Sun protection beyond sunscreen
Sunscreen is just one part of sun safety. Here’s more:
- Seek shade, especially during peak sun hours (10am-4pm)
- Wear protective clothing with a tight weave and a UPF rating
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses that block UVA and UVB rays
Make sun protection a priority
Sun protection is the most important thing you can do for healthy skin. Using sunscreen effectively and incorporating other sun-safe practices can significantly reduce your risk of skin damage and allow you to enjoy the summer worry-free.