Have you ever reached for an extra slice of pizza or a second serving of dessert, even though you’re already full? Or maybe you’ve felt sudden hunger pangs, right after eating? If the answer is yes, you’ve experienced the push and pull of leptin and ghrelin, your hunger hormones.
Understanding the delicate balance between leptin and ghrelin can be a game-changer in your weight management journey. These two hormones play a crucial role in regulating appetite and energy balance. Let’s delve deeper into how they work and how you can harness their power.
Leptin: The satiety hormone
Leptin, often referred to as the “satiety hormone,” is produced by the body’s adipose tissue, which we know as body fat. When you eat, your fat cells release leptin into your bloodstream, signaling your brain that you’re full. This signal helps reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure.
Why leptin resistance matters
Unfortunately, many people develop leptin resistance, a condition where the brain becomes less responsive to leptin’s signals. This can lead to increased appetite, cravings, and weight gain. Factors contributing to leptin resistance include:
- Chronic overeating: Consuming excessive calories can lead to elevated leptin levels, causing the brain to become desensitized.
- Poor sleep: Inadequate sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, including leptin production.
- Chronic stress: Stress hormones can interfere with leptin signaling.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can impair leptin’s ability to communicate with the brain.
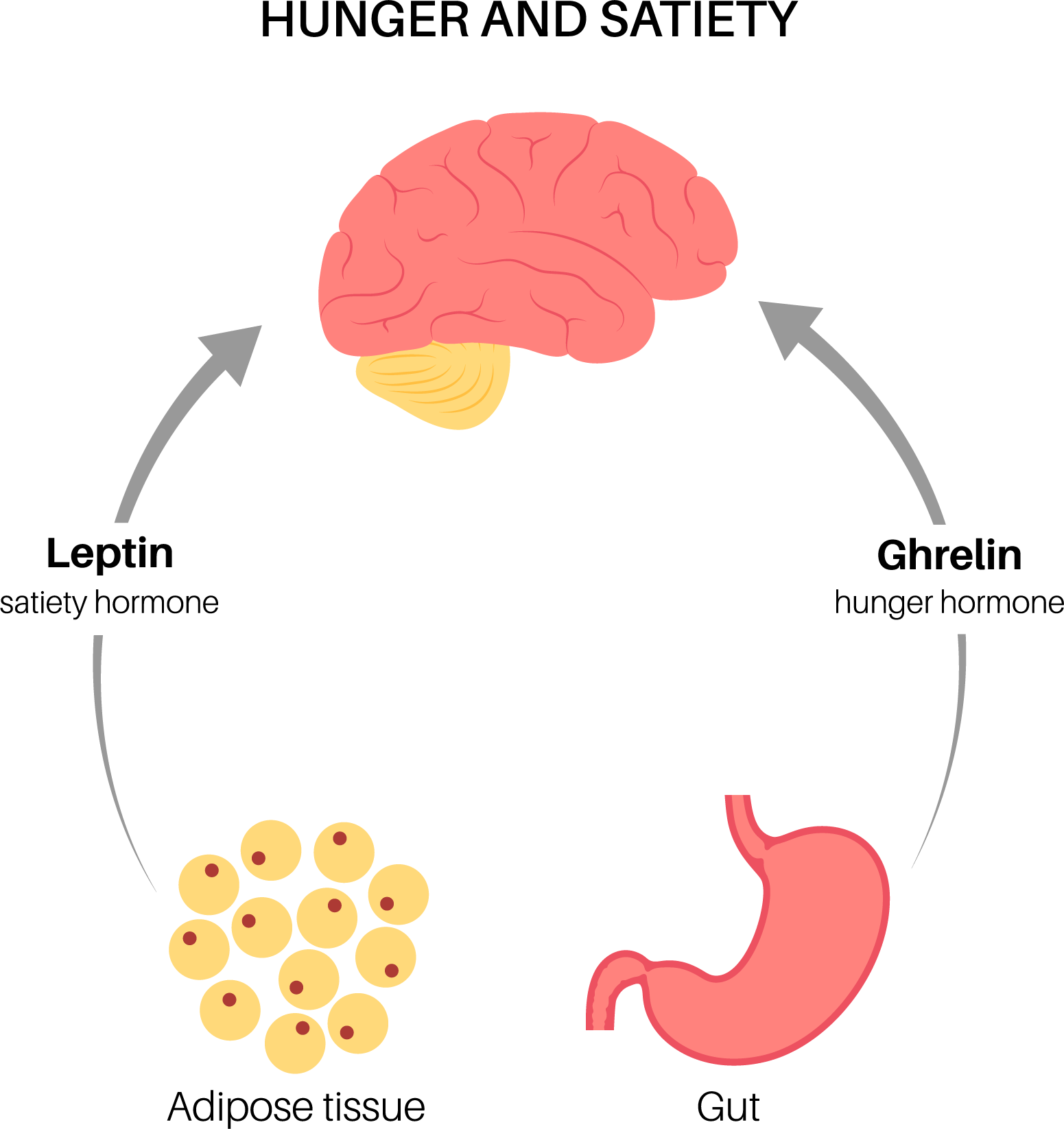
Ghrelin: The hunger hormone
Ghrelin, often called the “hunger hormone,” is produced primarily in the stomach (gut). It stimulates appetite by signaling the brain to release hunger hormones. Ghrelin levels typically rise before meals and decrease after eating.
Factors affecting ghrelin levels
Several factors can influence ghrelin levels:
- Meal timing and frequency: Irregular eating patterns can lead to increased ghrelin levels and hunger.
- Sleep: Inadequate sleep can elevate ghrelin levels, promoting overeating.
- Stress: Stress can increase ghrelin production, leading to increased appetite.
- Protein intake: Consuming adequate protein can help regulate ghrelin levels and reduce hunger.
Balancing leptin and ghrelin for optimal health
When leptin and ghrelin work together, you’re in the sweet spot for metabolic efficiency – which means a stronger, leaner you. When these hormones function harmoniously, appropriate hunger and satiety cues encourage healthier eating habits.
If your body’s intricate balance gets derailed, you risk heading toward a dangerous trio: obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease, all of which can be triggered by this internal mismatch. Therefore, adopting lifestyle strategies that support optimal hormone function is essential.
“It can be challenging to recognize our hunger and satiety cues and for some people, it becomes more challenging during the holiday season. Striving to make smart lifestyle choices such as prioritizing sleep, managing stress, and adopting a healthy diet can optimize our body’s natural hunger signals. Consider setting realistic goals for sleep, stress management and/or healthy eating with hopes these develop into lifelong habits.”
Danna Woods, RD, LD
Welia Health Registered Dietitian
1. Prioritize sleep
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to improve sleep quality.
- Avoid screens before bed, as the blue light can disrupt sleep patterns.
2. Manage stress
- Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
- Engage in hobbies and activities you enjoy.
- Seek professional help if stress becomes overwhelming.
3. Adopt a balanced diet
- Consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of unhealthy fats.
- Practice mindful eating, paying attention to hunger and fullness cues.
4. Stay active
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling.
- Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle mass.
- Find activities you enjoy to make exercise more sustainable.
5. Consider intermittent fasting
- Intermittent fasting (IF) can help regulate hormones, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss.
- Be sure to consult with your provider or dietitian before starting any new diet or fasting regimen.
Learn more about intermittent fasting by reading, Pros and Cons of Intermittent Fasting.
By following these strategies, you can help balance your leptin and ghrelin levels, improve your overall health, and achieve your weight management goals. Remember, sustainable weight loss and long-term health require a holistic approach that addresses both physical and mental well-being.
To meet with a Welia Health registered dietitian, call 320.679.1313. Appointments are available at Welia Health’s Mora and Pine City clinics. Note that a provider referral is required for a dietitian appointment. Contact your insurance carrier to confirm nutrition counseling is covered by your health plan.












